AP Computer Science :: Projects :: Gradebook
Problem
Electronic gradebooks are used by teachers to store grades on individual assignments and to calculate students’ overall grades. Yorkville teachers use the eSchool gradebook software to keep track of your grades.
Some teachers like to calculate grades based on what is sometimes called a "total points" system. This is the simplest way to calculate grades. A student's grade is the sum of the points earned on all assignments divided by the sum of the points available on all assignments. For example, suppose that a computer science class has a set of programming projects, quizzes, and tests, and that the sum of the points of all of these assignments is 485 for a semester. A student earns 412 of those points. His grade is 412/485, or about 84.95 percent.
In a total points system, teachers have to carefully figure out how many points each assignment should be worth, in order to make sure that certain assignments don’t dominate the students' grades. Some teachers don’t like to worry about the point value of each assignment, and they prefer what is sometimes called a "weighted category" system.
In a weighted category system, the teacher defines two or more categories and assigns a percentage weight value to each category. The sum of the weights adds up to 100. Grades are calculated by taking the average score of assignments in each category, multiplying each of those numbers by the weight for its category, and adding those values together.
For example, the computer science class described above could grade with a weighted category system by defining three categories: programming projects, quizzes, and tests. The teacher decides that programming projects should be worth 45 percent, quizzes 10 percent, and tests 45 percent. A student's average on programming projects is .95, on quizzes is .92, and on tests is .85. The student’s grade is:
PROJECTS QUIZZES TESTS GRADE (.95 × 45) + (.92 × 10) + (.85 × 45) = 90.2
Each value in parentheses is the portion of the total grade for one category. In this project, you will complete several classes to create an electronic gradebook that can calculate grades using either the total points system or the weighted category system. You will also write a client class to test your other classes.
Instructions
Download this project to start the Gradebook project.
Now that you understand the basics of gradebook software, let's take a look at the basic classes that will be used in this project. They have been designed for you, but it’s important that you understand the design before you attempt to write the code. Here are the classes used in this project, and the methods defined in each class:
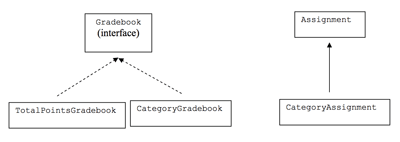
- Since we’re going to make more than one kind of gradebook, we will use an interface named Gradebook. The interface contains two methods: calculateGrade, which calculates a student’s grade according to the rules for the implementation of the Gradebook, and add, which adds a new assignment to the Gradebook.
- We have a TotalPointsGradebook class, which implements Gradebook and uses the total points system of calculating grades. This is the simpler implementation.
- We also have a CategoryGradebook class, which implements Gradebook and uses the weighted category system of calculating grades. This is the more difficult implementation.
- We have an Assignment class. An Assignment has a name, a number of points possible for the assignment, and a number of points earned for an assignment. The TotalPointsGradebook class has an ArrayList containing Assignment objects.
- We have a CategoryAssignment class. The CategoryAssignment class extends the Assignment class. It has everything that the Assignment class has. In addition, it has the name of the category to which this Assignment belongs. The CategoryGradebook class has an ArrayList containing CategoryAssignment objects.