Computer Security :: Lessons :: Digital Signatures
Properties of Digital Signatures
A digital signature uses public-key cryptography as a way to verify a message. The diagram below shows a generic model of the process of making and using digital signatures.
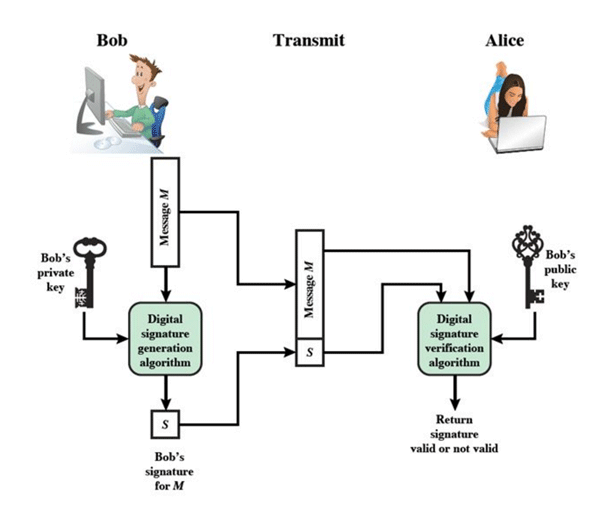
Message authentication can protect messages between two parties from a third party, but they do not protect those two parties against each other. Here are some forms of dispute that can arise:
- After receiving a message, the receiver could forge a different message and claim it is from the sender. The receiver would just have to create a message and append the sender's authentication code.
- The sender can deny sending the message since it is possible for the receiver to forge a message.
Because of these concerns a digital signature must have the following general properties:
- It must verify the author, date, and time of the signature.
- It must authenticate the contents at the time of the signature.
- It must be verifiable by third parties in order to resolve disputes.
The following attacks on digital signatures are listed in order of increasing severity, and will lead to more specific properties for a digital signature:
- Key-only attack: The attacker only knows the signature user's public key.
- Known message attack: The attacker is given access to a set of messages and their signatures.
- Generic chosen message attack: The attacker chooses a list of messages before attempting to break the signature scheme, which allows the attack to obtain valid signatures for those messages.
- Directed chosen message attack: Similar to the generic attack, but the list of messages to be signed is chosen after the attack knows the signature user's public key, but before any signatures are seen.
- Adaptive chosen message attack: The attack may request from the signature user signatures of messages that depend on previously obtained message-signature pairs.
Success at breaking a signature scheme occurs when the attacker does any of the following:
- Total break: THe attacker determines the user's private key.
- Universal forgery: The attacker finds an efficient signing algorithm that provides an equivalent way of constructing signatures on arbitrary messages.
- Selective forgery: The attacker forges a signature for a particular message chosen by the attacker.
- Existential forgery: The attacker forges a signature for at least one message that the attacker has no control over.
Digital Signature Requirements
Based on the properties and attacks already discussed, the following requirements are necessary for a valid digital signature:
- The signature must be a bit pattern that depends on the message being signed.
- The signature must use some information unique to the sender to prevent both forgery and denial.
- It must be relatively easy to produce the digital signature.
- It must be relatively easy to recognize and verify the digital signature.
- It must be computationally infeasible to forge a digital signature or by constructing a fraudulent digital signature for a given message.
- It must be practical to retain a copy of the digital signature in storage.
A direct digital signature is a digital signature scheme that involves only the communicating parties so it is assumed the destination knows the public key of the source. Confidentiality can be provided by encrypting the entire messages and signature with a shared secret key using symmetric encryption.
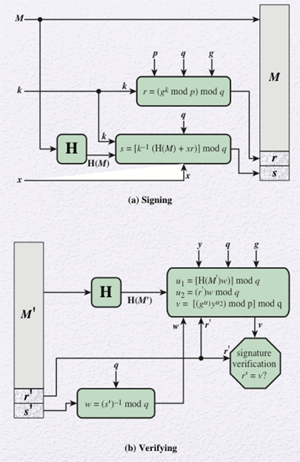
The Digital Signature Algorithm
The Digital Signature Algorithm, or DSA, is based on the difficulty of computing discrete logarithms. The DSA was published in 1991 by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and uses the Secure Hashing Algorithm (SHA). WHile it is a public-key technique, DSA cannot be used for encryption or key exchange. It is based on the ElGamal Digital Signature Scheme as well as the Schnorr Digital Signature Scheme.
RSA Algorithms
RSA Algorithms are widely used in the financial sector and are the most widely-used digital signature algorithm. The following video broadly explains how RSA works and the leadup to its development:



