Database Programming :: Lessons :: Database Management Systems
What is a Database?
A database is a collection of related data. That data can contain information that can be helpful in a variety of situations. Most major computer applications utilize databases to store information as databases are much better at scaling than a text file or spreadsheet.
Databases can be organized into tables that contain columns known as fields and rows called records. Watch the video below for more details about databases.
Database Management Systems
A database management system, or DBMS, is a program that allows users to more easily create and maintain databases. A DBMS should allow the user to define, construct, manipulating, and share a database.
Defining a database means specifying the data types of its fields, the structure of the tables in the database, and the constraints, or limits, placed on the data allowed in the database.
Constructing a database is the process of storing the data. This is typically handled by the DBMS so the user does not need to worry about where or how the data is stored.
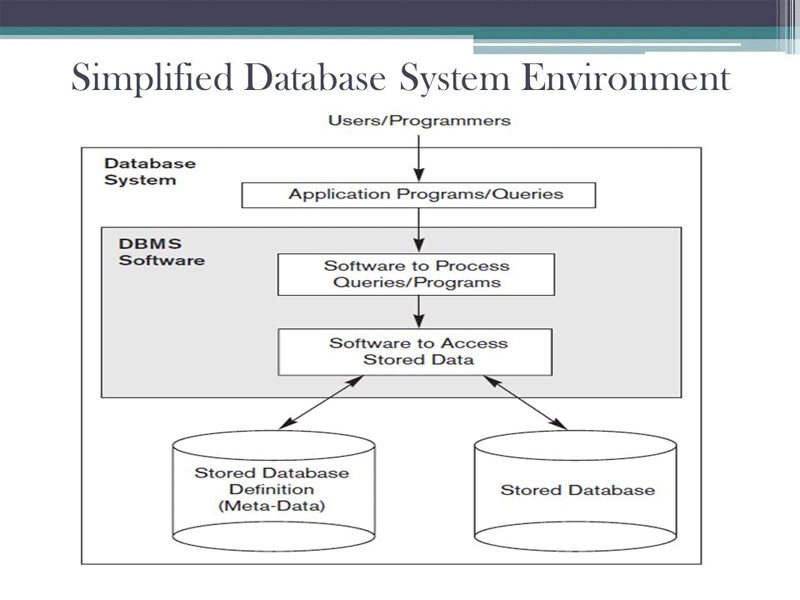
Manipulating a database can involve data retrieval as well as data updates.
Sharing a database allows multiple users to access the database at the same time. The DBMS will handle any conflicts that arise from multiple user updating information at the same time.
The main characteristics of a DBMS are the following:
- Self-describing nature of a database system.
- Insulation between programs and data.
- Multiple possible views of the data.
- Data sharing capabilities.
- Multiple user support.
While the above characteristics are the most essential, the following characteristics are also capabilities of a DBMS:
- Support for a data model that allows the user to view the data.
- Support for high-level languages that allow the user to define, access, and manipulate data.
- Transaction management that provides the capability for concurrent access to the database by multiple users.
- Access control that provides the ability to limit user access to certain actions or elements of the database.
- The ability to recover from system failures without losing data.
Database Terms
An instance of a database is the current contents of that database, or the state of the database. Alternatively, a schema is a plan for a database.
An example of a schema would be "Captain Name," "Ship Name," and "Birthday" while an example of an instance of that schema would be "James T. Kirk," "USS Enterprise," and "2233-03-22."
Data independence means the physical schema can be changed without changing the logical schema and vice a versa. The physical level is the actual data that resides in storage somewhere while the logical level is the data explained using a data model such as the relational data model.
A data control language (DCL) is used to grant access to specific commands. For example, a user may be able to view data, but not manipulate that data.
A data definition language (DDL) is used to dictate the schema of a database.
A data manipulation language (DML) is used to select, insert, delete, and update data in a database. The video below is a more detailed explanation of the differences among the three data language command types.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Databases
Some of the advantages of a database include the following:
- Controlled redundancy
- Less inconsistency
- Shared access to data
- Easier integrity maintenance
- Backup and recovery
Some of the disadvantages of a database include the following:
- More complex concurrency control
- More complex centralized access control
- Security necessary to allow sharing of data
- Necessary redundancies cause more complex updates



